What Makes PBN Sites Different from Other Websites?
In the world of SEO and digital marketing, the term PBN—short for Private Blog Network—is both powerful and controversial. A PBN is a network of websites used to build backlinks to a main website (also known as the “money site”) with the goal of improving its search engine rankings. At first glance, PBN sites may look like ordinary blogs or websites. However, they differ significantly from regular sites in structure, purpose, management, and long-term value.
This article will explore the major differences between PBN sites and other types of websites, including their goals, characteristics, risks, and SEO implications.
1. Purpose and Intent
PBN Sites:
The primary goal of a PBN site is to manipulate search engine rankings by creating backlinks to another site. These sites are built for SEO purposes, not for user engagement, brand development, or monetization through products or services. PBN sites exist to pass on link equity to other websites.
Other Sites (Legitimate Websites):
Regular websites—such as blogs, company sites, e-commerce platforms, or news portals—are designed to provide value to users, grow an audience, promote a brand, or sell products/services. Backlinks to other sites are natural and are usually a byproduct of content creation, not the central goal.
2. Content Quality and Originality
PBN Sites:
PBNs often rely on low to medium-quality content. Many use spun, AI-generated, or repurposed articles with minimal editing. Their goal is not to entertain or educate real users, but to keep the site looking somewhat legitimate in Google’s eyes while hosting backlinks.
Other Sites:
Legitimate sites invest in high-quality, original, and relevant content that addresses the needs and interests of their audience. These websites aim for engagement metrics such as time on site, shares, and user feedback, which contribute to organic growth.
3. Design and User Experience
PBN Sites:
Most PBN sites have basic or outdated designs, minimal branding, and generic layouts. The focus is on functionality over aesthetics. Many PBNs don’t prioritize mobile-friendliness, load speed, or user experience.
Other Sites:
Well-managed websites invest in professional design, UX/UI, branding, and optimization. These sites are meant to attract and retain users, drive conversions, and build trust with both users and search engines.
4. Ownership Transparency
PBN Sites:
A key feature of PBNs is anonymity and lack of transparency. The owner will often register domains under different names, use various hosting services, and hide WHOIS data to avoid detection by Google or other search engines.
Other Sites:
Legitimate websites typically have clear ownership. You can find contact pages, team bios, business addresses, and public WHOIS information. These details help build credibility and authority.
5. Hosting and IP Diversity
PBN Sites:
To avoid being flagged by search engines, PBN site owners often use different hosting companies, IP addresses, and server locations for each site in their network. This prevents Google from easily linking them together.
Other Sites:
Normal websites don’t need to hide their hosting environment. Many use mainstream services like Bluehost, GoDaddy, or SiteGround. Multiple sites from the same brand may even be hosted on the same server or IP address without SEO penalties.
6. Linking Practices
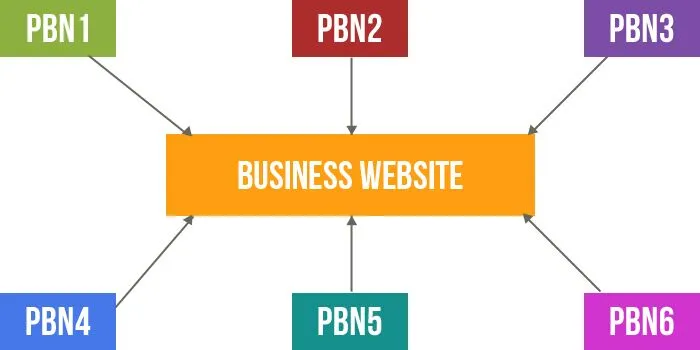
PBN Sites:
The defining trait of a PBN is aggressive outbound linking. These links are often keyword-optimized and unnatural, and they typically point to the same few money sites. There’s little to no editorial discretion—links are inserted purely for SEO manipulation.
Other Sites:
In contrast, authentic websites link out organically, based on relevance or to support their content. The ratio of outbound to internal links is balanced, and links are earned rather than placed intentionally.
7. Domain Acquisition Strategy
PBN Sites:
PBN owners often purchase expired domains with existing backlinks and authority metrics. The goal is to capitalize on the domain’s historical SEO value. These domains are then rebuilt quickly with filler content and links.
Other Sites:
Most legitimate sites use brand-new or branded domains, purchased with long-term use in mind. They focus on building domain authority over time through consistent publishing and outreach efforts.
8. Risk of Penalty
PBN Sites:
Using PBNs violates Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. If discovered, both the PBN sites and the money site can be penalized, leading to loss of rankings, deindexing, or even manual action reports.
Other Sites:
White-hat websites that follow SEO best practices are at minimal risk of penalties. In fact, they are more likely to benefit from algorithm updates focused on content quality, user trust, and natural link profiles.
Conclusion
While PBN sites may offer short-term gains in rankings, they are fundamentally different from regular websites in purpose, structure, and long-term value. Legitimate websites prioritize user experience, transparency, and sustainable SEO practices. In contrast, PBNs are engineered to manipulate algorithms, often at the cost of quality and ethical standards.
For businesses aiming to build a lasting online presence, focusing on real content, genuine outreach, and high-authority backlinks is the safer and more rewarding path. PBNs may still exist in the shadows of SEO, but the future of ranking success lies in authenticity, relevance, and trust.